MySQL 分层、存储引擎
mysql 分层
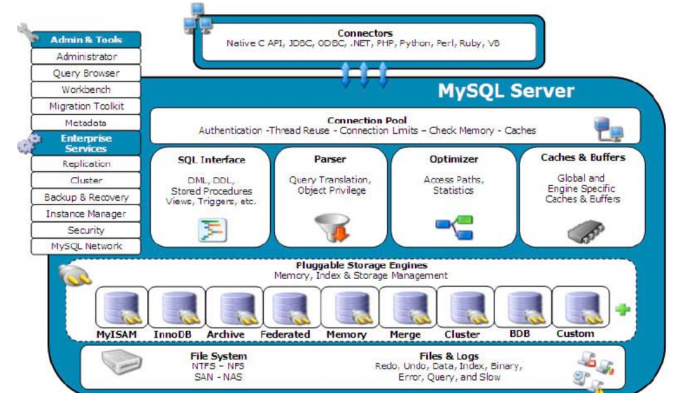
- 连接层
- 服务层
- 提供各种用户使用的接口
- 提供 SQL 优化器(MySQL Query Optimizer)
- 引擎层
- 提供各种存储数据的方式
- InnoDB
- MyISAM
- 存储层
InnoDB 和 MyISAM 区别
- InnoDB
- MyISAM
- 查询数据库支持哪些引擎
- 查询默认引擎
show variables like '%storage_engine%';
- 创建表时指定引擎
SQL 优化
原因
- 性能低
- 执行时间长
- 等待时间长
- SQL 语句欠佳(连接查询)
- 索引失效
- 服务器参数设置不佳
编写过程和解析过程的差异
- 编写过程
select distinct ... from ... join ... on ... where ... group by ... having ... order by ... limit
- 解析过程
from ... on ... join ... where ... group by ... having ... select distinct... order by ... limit
- 参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/annsshadow/p/5037667.html
优化索引
- 索引是帮助 MYSQL 高效获取数据的数据结构
- 索引一般采用树结构
- 索引弊端
- 索引本身需要空间
- 索引不适用
- 提高查询,降低增删改效率
- 优点
B 树与索引
- 三层 B 树可以存放百万级别数据
- B 树一般都是指 B+ 树
- B + 树中查找数据的次数
索引
分类
创建索引
方式一
create 索引类型 索引名 on 表(字段)- 单值索引
create index dept_index on tb(dept);
- 唯一索引
create unique index name_index on tb(name);
- 复合索引
create index dept_name_index on tb(dept, name);
方式二
- 单值
alter table tb add index dept_index(dept);
- 唯一
alter table tb add unique index name_index(name);
- 复合
alter table tb add index dept_name_index(dept, name);
- DDL 语句不需要 commit; 自动提交
- 如果一个字段是 primary key,该字段默认是主键索引
删除索引
- drop index 索引名 on 表名;
drop index name_index on tb;
查询索引
- show index from 表名
show index from tb;
SQL性能问题
- 分析 sql 执行计划
- explain
- 可以模拟 SQL 优化器执行 SQL 语句
- MYSQL 查询优化会干扰我们的优化
SQL优化准备
- explain SQL 语句
- id 编号
- select_type 查询类型
- table 表名
- type 类型
- possible_keys 预测用到的索引
- key 实际用到的索引
- key_len 实际使用索引的长度
- ref 表之间的引用
- rows 通过索引查询到的数据量
- Extra 额外信息
explain中的id、 table
id 值相同
- id 值相同,从上往下,顺序执行
- 表的执行顺序,跟随数据量变化,原理是笛卡尔积
- 数据量小的表优先查询
查询课程编号为2或教师编号为3的老师的信息
1
2
|
explain select t.* from teacher t, course c, teacherCard tc
where t.tid=c.tid and t.tid=tc.tcid and (c.cid = 2 or tc.tcid=3);
|
查询教授SQL课程的老师的描述信息
1
2
|
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacherCard tc, course c, teacher t
where c.tid = t.tid and t.tcid = tc.tcid and c.cname='sql';
|
id值不同
- id 值不同,id 值大的优先查询
- 本质:在嵌套子查询时,先查内层,再查外层
查询教授SQL课程的老师的描述信息
子查询形式
1
2
3
4
|
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacherCard tc where tc.tcid=
(select t.tcid from teacher t where t.tid =
(select c.tid from course c)
);
|
id值相同 + id值不同
查询教授SQL课程的老师的描述信息
多表 + 子查询形式
1
2
|
explain select t.tname, tc.tcdesc from teacher t, teacherCard tc
where t.tcid=tc.tcid and t.tid=(select c.tid from course c where cname='sql');
|
select_type
- primary 包含子查询 SQL 中的主查询(最外层)
- SUBQUERY 包含子查询 SQL 中的子查询(非最外层)
- simple 简单查询,不包含子查询和 union
- derived 衍生查询,使用到了临时表
- from 子查询中只有一张表
explain select cr.cname from (select * from course where tid in (1, 2)) cr;
- from 子查询中,如果有 table1 union table2,table1 就是 derived
explain select cr.cname from (select * from course where tid=1 union select * from course where tid =2) cr;
- union result
Type级别
system
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
create table test01
(
tid int(3),
tname varchar(20)
);
alter table test01 add constraint tid_pk primary key(tid);
insert into test01 values(1, 'a');
explain select * from (select * from test01) t where tid=1;
|
- system>const>eq_ref>ref>range>index>all
- system 和 const 只是理想情况,一般优化很难达到
- system 只有一条数据的系统表,或衍生表只有一条数据的主查询
const
1
2
3
4
5
|
explain select tid from test01 where tid=1;
/* 删除 primary 索引 */
alter table test01 drop primary key;
/* 修改索引为一般索引 */
create index test01_index on test01(tid);
|
- const 只能查到一条数据的 SQL
- 只能用于 primary key 或 unique 索引
- 如果是一般索引,不会出现 const
eq_ref
1
2
3
4
|
alter table teacherCard add constraint pk_tcid primary key(tcid);
alter table teacher add constraint uk_tcid unique index(tcid);
delete from teacher where tcid>3;
explain select t.tcid from teacher t, teacherCard tc where t.tcid = tc.tcid;
|
- 对于每个索引键的查询,返回匹配有且只有一行数据()有且只有一个不能多,也不能为0)
- 常见于唯一索引和主键索引
- 上述语句用到的索引是 teacher 表的 tcid 字段
- 如果 teacher 表的数据个数和连接查询的数据个数一致,才有可能满足 eq_ref 级别
ref
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
insert into teacher values(4, 'tz', 4);
insert into teacherCard values(4, 'tzc');
alter table teacher add index index_name(tname);
explain select * from teacher where tname='tz';
|
- 非唯一索引
- 对于每个索引键的查询,返回匹配的所有行(0, 多)

range
1
2
3
|
alter table teacher add index tid_index(tid);
explain select t.* from teacher t where t.tid <3;
|
- 检索指定范围的行,where 后面是一个范围查询
between, in, <, >, >=, <=- 特殊:
in 查询,有时会失效,从 range 级别转为 all 无索引级别
index, all
1
2
3
4
|
/* tid 有索引,只扫描 tid 列 */
explain select tid from teacher;
/* course 表无索引,扫描全部数据 */
explain select cid from course;
|

tid是索引,只需要扫描索引表, 不需要扫描所有表中的所有的数据;;
cid不是索引,需要全表扫描, 即需要所有表中的所有数据;
- index 查询全部索引数据
- all 查询全部数据
总结
- system/const
- eq_ref
- ref
- 结果多条
- 每条数据可能是多条(每条数据是0或者多条)
possible_keys, key
possible_keys 可能用到的数据,是一种预测, 不准;
key: 实际用到的索引;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
alter table course add index cname_index(cname);
explain select t.tname, tc.tcdesc from teacher t, teacherCard tc
where t.tcid=tc.tcid and t.tid=(select c.tid from course c where cname='sql');
explain select tc.tcdesc from teacherCard tc, course c, teacher t
where c.tid = t.tid and t.tcid = tc.tcid and c.cname='sql';
|

key_len
作用: 用于判断复合索引是否被完全引用;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
create table test_kl
(
name char(20) not null default ''
);
alter table test_kl add index index_name(name);
explain select * from test_kl where name='';
alter table test_kl add column name1 char(20);
alter table test_kl add index index_name1(name1);
explain select * from test_kl where name1='';
drop index index_name on test_kl;
drop index index_name1 on test_kl;
alter table test_kl add index name_name1_index (name, name1);
explain select * from test_kl where name1='';
alter table test_kl add column name2 varchar(20);
alter table test_kl add index name2_index(name2);
/* key_len=63 = 60+1(null)+2(varchar) */
explain select * from test_kl where name2='';
|
- 索引的长度
- 用于判断复合索引是否被完全使用
- utf8 中,1 个字符占 3 个字节
- gbk 中,1 个字符 2 个字节
- latin 中,1 个字符 1 个字节
- 如果索引字段可以为 null,mysql 底层会用 1 个字节用于标识
- 索引字段为 varchar,用 2 个字节代表可变长度
ref
注意用type中的ref值区分;
作用: 指明当前表所参照的字段。
select … where a.c = b.x; (其中b.x可以是常量, const)
1
2
3
|
alter table course add index tid_index(tid);
explain select * from course c, teacher t where c.tid = t.tid and t.tname='tw';
|
rows
被索引优化查询的 数据个数;
1
|
explain select * from course c, teacher t where c.tid = t.tid and t.tname='tz';
|
using filesort
性能消耗大; 需要“额外”的一次排序; (查询)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
create table test02
(
a1 char(3),
a2 char(3),
a3 char(3),
index idx_a1(a1),
index idx_a2(a2),
index idx_a3(a3)
);
/* 排序和查找不是同一个字段 Using filesort */
explain select * from test02 where a1 = '' order by a2;
drop index idx_a1 on test02;
drop index idx_a2 on test02;
drop index idx_a3 on test02;
alter table test02 add index idx_a1_a2_a3(a1, a2, a3);
/* 复合索引跨列 */
explain select * from test02 where a1='' order by a3;
explain select * from test02 where a2='' order by a3;
explain select * from test02 where a1='' order by a2;
|
- 性能消耗大,需要额外一次排序或查询
- 如果排序和查找不是同一个字段,则会出现 Using filesort
- 如果复合索引跨列,会出现 Using filesort
- where 和 order by 按照符合索引的顺序使用,不要跨列或无序
- 常见于 order by语句中;

复合索引, 不能跨列(最佳左前缀)
where哪些字段, 就order by哪些字段;
using temporary
1
|
explain select a1 from test02 where a1 in ('1', '2', '3') group by a2;
|
using index
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
explain select a1, a2 from test02 where a1='' or a2='';
drop index idx_a1_a2_a3 on test02;
alter table test02 add index id_a1_a2(a1, a2);
explain select a1, a3 from test02 where a1='' or a3='';
/* 对 possible_keys 和 key 的影响 */
explain select a1, a2 from test02 where a1='' or a2='';
explain select a1, a2 from test02;
|
原因: 性能提升, 不读取源文件, 只从索引文件中获取数据, 只要使用到的列, 全部都在索引中, 就是索引覆盖到using index;
-
使用到的列都在索引中,称为索引覆盖。
-
性能提升
-
不读取原文件,只从索引文件中获取数据
-
不需要回表查询
-
索引覆盖对 possible_keys 和 key 的影响
- 如果没有 where,则索引只出现在 key 中
- 如果有 where,则索引出现在 key 和 possible_keys 中;
例如, test02表中有一个复合索引(a1,a2,a3)
explain select a1,a2 from test02 where a1=’’ or a2= ‘’;
using where
需要回表查询;
假设age是索引列, 但查询语句select age, name from … where age = …, 此语句中必须回原表查Name, 因此会显示
explain select a1, a3 from test02 where a3 = ‘’; –a3需要回原表查询;
impossible where
1
|
explain select * from test02 where a1='x' and a1='y';
|
where子句永远为false;
优化示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
create table test03
(
a1 int(4) not null,
a2 int(4) not null,
a3 int(4) not null,
a4 int(4) not null
);
alter table test03 add index idx_a1_a2_a3_a4(a1, a2, a3, a4);
/* Using index */
/* 推荐按照复合索引的顺序查询 */
explain select a1, a2, a3, a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a2=2 and a3=3 and a4=4;
/* Using index */
/* 经过 SQL 优化器后,效果与上一个查询语句一致 */
explain select a1, a2, a3, a4 from test03 where a4=1 and a3=2 and a2=3 and a1=4;
/* Using where; Using index */
/* a4 跨列,索引失效,造成回表查询 */
/* where a1=1 and a2=2 ... order by a3 仍然遵循复合索引的顺序,因此有 Using index */
explain select a1, a2, a3, a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a2=2 and a4=4 order by a3;
/* Using where; Using index; Using filesort */
/* where a1=1 ... order by a3 跨列,多了一次查找/排序,出现 Using filesort */
explain select a1, a2, a3, a4 from test03 where a1=1 and a4=4 order by a3;
|
– 总结:
i. 如果是(a,b,c,d)复合索引, 和 使用的顺序全部一致, 则复合索引全部使用; 如果部分一致,则:
select a, c where a = . and b = . and c = . and d = .;
ii.where和order by在一起不要跨列;
单表优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
create table book
(
bid int(4) primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
authorid int(4) not null,
publicid int(4) not null,
typeid int(4) not null
);
insert into book values(1, 'java', 1, 1, 2);
insert into book values(2, 'html', 2, 1, 2);
insert into book values(3, 'sql', 3, 2, 1);
insert into book values(4, 'C', 4, 4, 3);
commit;
/* type:All*/
/* Using where; Using filesort */
explain select bid from book where typeid in(2, 3) and authorid=1 order by typeid desc;
/* type:index */
/* Using where; Using index; Using filesort */
alter table book add index idx_bta(bid, typeid, authorid);
/* 为避免干扰,优化之前删除老的索引 */
drop index idx_bta on book;
/* 根据 sql 实际解析的顺序,调整索引顺序 */
/* type:index */
/* Using where; Using index */
alter table book add index idx_tab(typeid, authorid, bid);
/* 删除索引,创建新索引测试 */
drop index idx_tab on book;
/* 将出现范围查询的字段 typeid 放到后面 */
alter table book add index idx_atb(authorid, typeid, bid);
/* 将范围查询 typeid in (2, 3) 放到 authorid=1 后面 */
/* type:ref */
/* Using where; Using index */
/* key_len: 4 */
explain select bid from book where authorid=1 and typeid in(2, 3) order by typeid desc;
/* Using index */
/* key_len: 8 */
/* typeid in(2, 3) 改为 typeid=3,不使用范围查询,typeid 索引有效 */
/* 通过 key_len 也可以佐证,此处有 2 个索引,typeid 索引有效 */
explain select bid from book where authorid=1 and typeid=3 order by typeid desc;
|
小结
- 索引不能跨列使用,保持索引定义和使用顺序一致性(最佳左前缀匹配);
- 索引需要逐步优化;
- 将含 in 的范围查询放到条件最后,防止整个索引失效;
- Using index
where authorid=1 ... authorid 在索引中,不需要回原表;
- Using where
... and typeid in (2,3) typeid 在索引中,但是使用了 in 范围查询,索引失效,需要回原表;
两表优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
create table teacher2
(
tid int(4) primary key,
cid int(4) not null
);
insert into teacher2 values(1, 2);
insert into teacher2 values(2, 1);
insert into teacher2 values(3, 3);
create table course2
(
cid int(4),
cname varchar(20)
);
insert into course2 values(1, 'java');
insert into course2 values(2, 'python');
insert into course2 values(3, 'kotlin');
commit;
/* 左连接,将数据量少的表放到左边 */
/* type:All */
/* Extra: */
/* type:All */
/* Extra: Using where; Using join buffer */
select * from teacher2 t left outer join course2 c
on t.cid=c.cid where c.cname='java';
/* 增加索引 */
/* type: index */
/* Extra: Using index */
/* type: All */
/* Extra: Using where; Using join buffer*/
alter table teacher2 add index index_teacher2_cid(cid);
/* type: ref */
/* Extra: Using where */
/* type: ref */
/* Extra: Using index*/
alter table course2 add index index_course2_cname(cname);
|
左连接:
select * from teacher2 t left join course2 c on t.cid = c.cid where c.cname = ‘java’;
对于两张表, 索引应该怎么加?—— 小表驱动大表;
—— 索引建立在经常使用的字段上;(由t.cid=c.cid可知, t.cid字段使用频繁, 因此给该字段加索引)
举个例子:
小表: 10
大表: 300
where 小表.x 10 = 大表.y 300; —— 循环了几次? 10
大表.y 300 = 小表.x 10 —— 循环了300次;
当编写… on t.cid = c.cid时,将数据量小的表 放左边; (假设此时t表数据量小)
using join buffer: extra中的一个选项, 作用: Mysql引擎使用了 连接缓存。(实际上是底层优化了你的sql, 你的sql写的比较差)
(3) 实际上对于三张表, 优化A,B,C
a.小表驱动大表; b.索引建立在经常查询的字段上;
小结
- 索引添加原则
- 小表驱动大表
- 索引建立在经常使用的字段上
- 三表或更多表使用相同的原则
- 左外连接,给左表加索引
- 右外连接,给右表加索引
- Using join buffer
避免索引失效的一些原则:
-
复合索引,不要跨列或无序使用(最佳左前缀)
-
复合索引, 尽量使用全索引匹配
-
不要在索引上进行任何操作
- 计算
- 函数
- 类型转换
- 如
... where a.x*3
select .. where A.x = .. ; —— 假设A.x是索引,
不要, select … where A.x * 3 = ..;
-
复合索引,左边索引失效,所有索引失效
-
复合索引使用不等于或者 is null,自身索引会失效,右侧索引可能会失效
-
MySQL 本身有 sql 优化器,实际优化效果并非百分之百达到预期
SQL优化, 是一种概率层面的优化。 至于是否使用了我们的优化, 需要用explain进行推测;
体验概率情况(<>, =), 原因是服务层里面有SQL优化器, 可能会影响我们的优化;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
mysql> drop index idx_typeid on book;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> drop index idx_authorid on book;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.15 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> alter table book add index idx_book_at (authorid, typeid);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ref | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 8 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | ref | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 8 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+-------------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid > 1 and typeid = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | range | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 4 | NULL | 3 | 25.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid = 1 and typeid > 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | range | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 8 | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid < 1 and typeid = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | range | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 4 | NULL | 1 | 25.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from book where authorid < 4 and typeid = 2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | book | NULL | range | idx_book_at | idx_book_at | 4 | NULL | 3 | 25.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+-------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql>
|
补救: 尽量使用索引覆盖(using index);
(a,b,c)
select a,b,c from xx. where a = .. and b = ..;
(5) like尽量以“常量 ”开头, 不要以’%‘开头, 否则索引失效;
(6)尽量不要使用类型转换(显式, 隐式):
explain select * from teacher where tname = ‘abc’;
// 程序底层将123 -> ‘123’, 即进行了类型转换;
explain select * from teacher where tname = 123;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
mysql> explain select * from teacher where tname = 'abc';
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | teacher | NULL | ref | index_name | index_name | 83 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from teacher where tname = 123;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | teacher | NULL | ALL | index_name | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 3 warnings (0.36 sec)
|
(7) 尽量不要使用or, 否则索引会失效;
select * from teacher where tname = ’’ and tcid > 1;
explain select * from teacher where tname = ’’ or tcid > 1; – 将or左侧的tname失效;
常见的优化方法
(8)一些其他的优化方法
exist和in
select … from table where exist in (子查询);
1
2
3
4
5
|
/* 有数据 */
select tname from teacher where exists(select * from teacher);
/* 无数据 */
select tname from teacher where exists(select * from teacher where tid=9999);
|
如果主查询的数据集大,则使用In;
如果子查询的数据集大, 则使用exist;
exist语法: 将主查询的结果, 放到子查询结果中进行条件校验(是否有数据, 如果有数据, 则校验成功), 如果符合检验,则保留数据;
select tname from teacher where exists (select * from teacher);
— 等价于select tname from teacher;
1
2
|
mysql> select tname from teacher where exists (select * from teacher where tid = 9999);
Empty set (0.00 sec)
|
in:
select … from table where tid in (1,3,5);
小结:
- 如果主查询数据集大,使用 in
- 如果子查询数据集大,使用 exist
- 将主查询的结构放到子查询结果中进行条件校验
- 如果子查询有数据,则校验成功
- 如果符合校验,则保留数据
Order by优化
- Using filesort
- 双路排序 MySQL 4.1 之前
- 扫描 2 次磁盘
- 第 1 次
- 从磁盘读取排序字段
- 对排序字段进行排序
- 在 buffer 中进行排序(buffer缓冲区进行排序)
- 第 2 次:扫描其他字段
- 单路排序
- 一次性读取全部磁盘
- 在 buffer 中进行排序
- 不一定是真正的单路,仍然可能是多次 IO
- 单路排序比双路排序占用更多 buffer
- 调整 buffer
set max_length_for_sort_data=1024
- 单路自动切换到双路的条件 (太低)
- 需要排序的列总大小超过
set max_length_for_sort_data=1024 定义的字节数
- 提供 order by 查询效率的策略
- 选择使用单路,双路; 调整 buffer 容量大小
- 避免使用
select * ...
- 复合索引避免跨列
- 保证全部排序字段 排序的一致性(都是升序或者降序)
SQL慢查询 - 慢查询日志: MySQL提供的一种日志记录, 用于记录MySQL中响应时间超过阀值的SQL语句(long_query), 慢查询日志默认是关闭的; 建议开发调优是打开, 而最终部署时候是关闭;
检查是否开启了慢查询日志; show variables like ‘%slow_query_log%’;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+-------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+-------------------------------------+
| slow_query_log | OFF |
| slow_query_log_file | D:\Software\mysql\Data\wjq-slow.log |
+---------------------+-------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.35 sec)
|
临时开启:
set global slow_query_log = 1; – 在内存中开启
exit
service mysql restart;
永久开启:
/etc/my.cnf文件里面配置;
[mysqld]
slow_query_log = 1;
slow_query_log _file= /var/lib/mysql/localhost-slow.log;
小结
- MySQL 用于记录响应时间超过阈值的 SQL 语句
long_query_time 阈值默认 10 秒- 慢查询日志默认关闭
- 建议在调优时打开,部署上线时关闭
- 检查是否开启了慢查询日志
show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
- 开启慢查询日志
- 临时开启
set global slow_query_log =1;- mysql 服务重启后失效
- 永久开启
vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld] slow_query_log=1 slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysql/localhost-slow.log
- 慢查询阈值修改
show variables like '%long_query_time%'; - 临时修改(临时设置阀值)
set global long_query_time=5; - 重新登录后生效
- 永久修改(永久设置阀值)
vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld] long_query_time=3
慢查询优化
慢查询日志
- MySQL 用于记录响应时间超过阈值的 SQL 语句
long_query_time 阈值默认 10 秒- 慢查询日志默认关闭
- 建议在调优时打开,部署上线时关闭
- 检查是否开启了慢查询日志
show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
- 开启慢查询日志
- 临时开启
set global slow_query_log =1;- mysql 服务重启后失效
- 永久开启
vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld] slow_query_log=1 slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysql/localhost-slow.log
- 慢查询阈值修改
show variables like '%long_query_time%'; - 临时修改
set global long_query_time=5; - 重新登录后生效
- 永久修改
vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld] long_query_time=3
慢查询阈值和mysqldumpslow工具查看慢SQL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/* 模拟慢查询 */
select sleep(5);
select sleep(4);
select sleep(3);
/* 获取返回记录最多的 3 个 SQL */
mysqldumpslow -s r -t 3 /var/lib/mysql/bigdata01-slow.log
/* 获取访问次数最多的 3 个 SQL */
mysqldumpslow -s c -t 3 /var/lib/mysql/bigdata01-slow.log
/* 按照时间排序,前 10 条包含 left join 查询语句的 SQL */
mysqldumpslow -s t -t 10 -g "left join" /var/lib/mysql/bigdata01-slow.log
|
- mysqldumpslow
- 常用参数
- s: 排序方式
- r: 逆序
- l: 锁定时间
- g: 正则匹配模式
- 标准语法
mysqldumpslow 各种参数 慢查询日志文件路径
– 获取返回记录最多的3个SQL;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
root@946bb7e7ee77:/# mysqldumpslow -s r -t 3 /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Reading mysql slow query log from /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Count: 2 Time=5.00s (10s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=1.0 (2), root[root]@[192.168.163.1]
select sleep(N)
Count: 1 Time=0.00s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), 0users@0hosts
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
# Time: N N:N:N
# User@Host: root[root] @ [N.N.N.N] Id: N
# Query_time: N.N Lock_time: N.N Rows_sent: N Rows_examined: N
SET timestamp=N;
select sleep(N)
Died at /usr/bin/mysqldumpslow line 167, <> chunk 3.
|
– 获取访问次数最多的3个SQL;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
root@946bb7e7ee77:/# mysqldumpslow -s c -t 3 /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Reading mysql slow query log from /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Count: 2 Time=5.00s (10s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=1.0 (2), root[root]@[192.168.163.1]
select sleep(N)
Count: 1 Time=0.00s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), 0users@0hosts
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
# Time: N N:N:N
# User@Host: root[root] @ [N.N.N.N] Id: N
# Query_time: N.N Lock_time: N.N Rows_sent: N Rows_examined: N
SET timestamp=N;
select sleep(N)
Died at /usr/bin/mysqldumpslow line 167, <> chunk 3.
root@946bb7e7ee77:/#
|
– 按照时间排序, 前10条包含left join查询语句的SQL;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
root@946bb7e7ee77:/# mysqldumpslow -s t -t 10 "left join" /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Reading mysql slow query log from left join /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77-slow.log
Can't open left join: No such file or directory at /usr/bin/mysqldumpslow line 97.
Count: 2 Time=5.00s (10s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=1.0 (2), root[root]@[192.168.163.1]
select sleep(N)
Count: 1 Time=0.00s (0s) Lock=0.00s (0s) Rows=0.0 (0), 0users@0hosts
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
mysqld, Version: N.N.N (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
# Time: N N:N:N
# User@Host: root[root] @ [N.N.N.N] Id: N
# Query_time: N.N Lock_time: N.N Rows_sent: N Rows_examined: N
SET timestamp=N;
select sleep(N)
Died at /usr/bin/mysqldumpslow line 167, <> chunk 3.
|
分析海量数据
a.模拟海量数据 存储过程 (无return) / 存储函数(有return)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
create database testdata;
use testdata;
create table dept
(
dno int(5) primary key default 0,
dname varchar(20) not null default '',
loc varchar(30) default ''
) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
create table emp
(
eid int(5) primary key,
ename varchar(20) not null default '',
job varchar(20) not null default '',
deptno int(5) not null default 0
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
|
通过存储函数, 插入海量数据;
创建存储函数;
b.创建存储 函数;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
use testdata;
delimiter $
create function randstring(n int) returns varchar(255)
begin
declare all_str varchar(100) default 'abcdefghijklmnopqrestuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
declare return_str varchar(255) default '';
declare i int default 0;
while i<n
do
set return_str=concat(return_str, substring(all_str, FLOOR(1+rand()*52), 1));
set i=i+1;
end while;
return return_str;
end $
|
冲突与解决
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
/* 开启慢查询日志,再创建存储过程/存储函数,报如下错误 */
/* ERROR 1418 (HY000):
This function has none of DETERMINISTIC, NO SQL, or READS SQL DATA
in its declaration and binary logging is enabled
(you *might* want to use the less safe log_bin_trust_function_creators variable) */
/* 临时解决 */
show variables like '%log_bin_trust_function_creators%';
set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;
|
永久解决
vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld] log_bin_trust_function_creators=1
通过存储函数插入随机整数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
use testdata;
delimiter $
create function ran_num() returns int(5)
begin
declare i int default 0;
set i=floor(rand()*100);
return i;
end$
|
通过存储过程插入海量数据
emp表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
delimiter $
create procedure insert_emp(in eid_start int(10), in data_times int(10))
begin
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit =0;
repeat
insert into emp values(eid_start+i, randstring(5), 'other', ran_num());
set i=i+1;
until i=data_times
end repeat;
commit;
end $
|
dept表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
delimiter $
create procedure insert_dept(in dno_start int(10), in data_times int(10))
begin
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit =0;
repeat
insert into dept values(dno_start+i, randstring(6), randstring(8));
set i=i+1;
until i=data_times
end repeat;
commit;
end $
|
插入数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
delimiter ;
call insert_emp(1000, 800000);
call insert_dept(10, 30);
/* 验证插入数据量 */
select count(1) from emp;
|
分析海量数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
show variables like '%profiling%';
/* profiling 影响性能,在部署实施前,应关闭此项 */
set profiling=on;
/* 记录 profiling 打开之后的所有 SQL 语句消耗的时间 */
show profiles;
/* 精确查询更多详情,Query_Id 参考上个语句的查询结果 */
show profile all for query 2;
show profile cpu, block io for query 2;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
mysql> call insert_emp(1000, 800000);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (24.61 sec)
mysql> call insert_dept(10, 30);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(1) from emp;
+----------+
| count(1) |
+----------+
| 800000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.15 sec)
|
分析海量数据: profiles
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
mysql> show profiles;
Empty set
mysql> show variables like '%profiling%';
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | OFF |
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> set profiling = on;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show profiles;
Empty set
mysql> show variables like '%profiling%';
+------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------------+-------+
| have_profiling | YES |
| profiling | ON |
| profiling_history_size | 15 |
+------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> show profiles;
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------+
| 1 | 0.00036875 | show variables like '%profiling%' |
+----------+------------+-----------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.04 sec)
|
小结
(1) profiles
show profiles; —— 默认是关闭的;
show variables like ‘%profiling%’ ;
set profiling = on;
show profiles; – 打开后, 会记录所有profiling打开之后的,全部SQL查询语句所花费的时间。缺点: 不够精确, 是总的时间;
(2) – 精确分析: sql诊断;
show profile all for query 上一步查询的Query Id
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
mysql> show profile all for query 2;
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+-------------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------+-----------------------+------------------+-------------+
| Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Context_voluntary | Context_involuntary | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out | Messages_sent | Messages_received | Page_faults_major | Page_faults_minor | Swaps | Source_function | Source_file | Source_line |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+-------------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------+-----------------------+------------------+-------------+
| starting | 0.000053 | 0.000044 | 0.000009 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| checking permissions | 0.000007 | 0.000005 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | check_access | sql_parse.cc | 5325 |
| Opening tables | 0.000013 | 0.000010 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | open_tables | sql_base.cc | 5118 |
| init | 0.000009 | 0.000007 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_prepare_select | sql_select.cc | 1058 |
| System lock | 0.000005 | 0.000004 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_lock_tables | lock.cc | 311 |
| optimizing | 0.000003 | 0.000003 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | optimize | sql_optimizer.cc | 146 |
| statistics | 0.000007 | 0.000006 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | optimize | sql_optimizer.cc | 372 |
| preparing | 0.000006 | 0.000005 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | optimize | sql_optimizer.cc | 495 |
| executing | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | exec | sql_executor.cc | 117 |
| Sending data | 0.111730 | 0.111738 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | exec | sql_executor.cc | 197 |
| end | 0.000025 | 0.000016 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_execute_select | sql_select.cc | 1113 |
| query end | 0.000005 | 0.000006 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_execute_command | sql_parse.cc | 5023 |
| closing tables | 0.000057 | 0.000058 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_execute_command | sql_parse.cc | 5072 |
| freeing items | 0.000138 | 0.000137 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | mysql_parse | sql_parse.cc | 6604 |
| cleaning up | 0.000011 | 0.000011 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | dispatch_command | sql_parse.cc | 1843 |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+-------------------+---------------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+-------+-----------------------+------------------+-------------+
15 rows in set (0.06 sec)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
mysql> show profile cpu, block io for query 2;
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| starting | 0.000053 | 0.000044 | 0.000009 | 0 | 0 |
| checking permissions | 0.000007 | 0.000005 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| Opening tables | 0.000013 | 0.000010 | 0.000003 | 0 | 0 |
| init | 0.000009 | 0.000007 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| System lock | 0.000005 | 0.000004 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| optimizing | 0.000003 | 0.000003 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| statistics | 0.000007 | 0.000006 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| preparing | 0.000006 | 0.000005 | 0.000001 | 0 | 0 |
| executing | 0.000002 | 0.000001 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| Sending data | 0.111730 | 0.111738 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| end | 0.000025 | 0.000016 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| query end | 0.000005 | 0.000006 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| closing tables | 0.000057 | 0.000058 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| freeing items | 0.000138 | 0.000137 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
| cleaning up | 0.000011 | 0.000011 | 0.000000 | 0 | 0 |
+----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+
15 rows in set (0.06 sec)
|
全局查询日志
记录开启之后的全部SQL语句。
(这次全局的记录操作, 仅仅在调优和开发过程中, 在最终的生产部署中,一定要关闭,影响性能)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
show variables like '%general_log%';
/* 开启全局日志,记录开启之后的所有 SQL 语句 */
set global general_log=1; -- 开启全局日志
/* 将日志记入表中 */
set global log_output='table';
/* 设置后执行一条查询 */
select count(1) from dept;
/* 显示日志信息 */
select * from mysql.general_log;
/* 如果所有的log不放到表, 可以放到一个文件中,不妨到将日志记入文件 */
set global log_output='file';
/* 通过默认保存地址查看日志文件 */
cat /var/lib/mysql/bigdata01.log;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
mysql> show variables like '%general_log%';
+------------------+---------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+---------------------------------+
| general_log | OFF |
| general_log_file | /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77.log |
+------------------+---------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.03 sec)
mysql> set global general_log=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%general_log%';
+------------------+---------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+---------------------------------+
| general_log | ON |
| general_log_file | /var/lib/mysql/946bb7e7ee77.log |
+------------------+---------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.03 sec)
mysql> set global log_output='table';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(1) from emp;
+----------+
| count(1) |
+----------+
| 800000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.17 sec)
mysql> select * from mysql.general_log;
+---------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+
| event_time | user_host | thread_id | server_id | command_type | argument |
+---------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+
| 2021-07-17 08:05:21 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Init DB | testdata |
| 2021-07-17 08:05:21 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Query | select count(1) from dept |
| 2021-07-17 08:05:32 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Init DB | testdata |
| 2021-07-17 08:05:32 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Query | select * from mysql.general_log |
| 2021-07-17 08:05:59 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Init DB | testdata |
| 2021-07-17 08:05:59 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Query | select count(1) from emp |
| 2021-07-17 08:06:06 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Init DB | testdata |
| 2021-07-17 08:06:06 | root[root] @ [192.168.163.1] | 4 | 0 | Query | select * from mysql.general_log |
+---------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.05 sec)
|
- 开启 general_log 后,所有 SQL 会被记录到系统自带的
mysql.general_log 表中
锁机制
解决因资源共享, 而造成的并发问题;
分类
- 按操作类型分
- 读锁(共享锁)
- 写锁(互斥锁)
- 如果当前写操作没有完毕,则无法进行其他读操作、写操作。
- 按操作范围分
- 表锁
- 对整张表加锁
- 开销小,加锁快
- 无死锁
- 但锁的范围大,容易发生锁冲突
- 并发度低
- MyISAM 采用表锁
- 行锁
- 对一条数据加锁
- 开销大,加锁慢
- 容易出现死锁
- 锁的范围较小,不易发生锁冲突
- 高并发概率低
- InnoDB 存储引擎是行锁
- 页锁
表锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
/* MYSQL/SQLSERVER 支持自增,Oracle 需要借助于序列来实现自增 */
create table tablelock
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
) engine myisam;
insert into tablelock(name) values('a1');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a2');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a3');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a4');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a5');
/* 查看加锁情况 */
show open tables;
/* 加锁 */
lock table tablelock read;
/* 加锁后可以读 */
select * from tablelock;
/* 加锁后不能写 */
/* ERROR 1099 (HY000): Table 'tablelock' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated */
delete from tablelock where id=1;
/* 加锁后,当前会话不能对其他表进行读操作 */
/* ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'dept' was not locked with LOCK TABLES */
select count(1) from dept;
/* 加锁后,当前会话不能对其他表进行写操作 */
/* ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'dept' was not locked with LOCK TABLES */
insert into dept values(39,'xxxxxx', 'yyyyyyyy');
/* 释放锁 */
unlock tables;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
mysql> create table tablelock
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
) engine myisam;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tablelock(name) values('a1');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tablelock(name) values('a2');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tablelock(name) values('a3');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a4');
insert into tablelock(name) values('a5');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show open tables;
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
| Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked |
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
| testdata | dept | 0 | 0 |
| testdata | tablelock | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | general_log | 0 | 0 |
| db001 | t_book | 0 | 0 |
| testdata | emp | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | proc | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | event | 0 | 0 |
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
7 rows in set (0.04 sec)
|
会话: Session, 可以理解为每一个访问数据的dos命令行、 数据库客户端工具, 都是一个会话;
1) 加读锁;
会话0:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
mysql> lock table tablelock read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from tablelock; -- 可以读
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | a1 |
| 2 | a2 |
| 3 | a3 |
| 4 | a4 |
| 5 | a5 |
+----+------+
5 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> delete from tablelock where id=1; -- 不可以写(增删改)
1099 - Table 'tablelock' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated
// 其他表也读不了, 不可以读
mysql> select * from dept;
1100 - Table 'dept' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
// 也不可以写
mysql> delete from dept where dno=10;
1100 - Table 'dept' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
|
如果某一个会话, 对A表加了read锁, 则该会话可以对A表进行读操作, 不能进行写操作; 且该会话不可以对其他表进行读操作, 也不能进行写操作;
会话1(泛指其他会话):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
mysql> select * from tablelock; -- 读(查询)可以
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | a1 |
| 2 | a2 |
| 3 | a3 |
| 4 | a4 |
| 5 | a5 |
+----+------+
5 rows in set (0.04 sec)
--写操作会等待, 会“等待”到会话0将锁释放
mysql> delete from tablelock where id = 1; -- 一直在等待
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
mysql> select * from dept; -- 对其他表可以读 (查询)
+-----+--------+----------+
| dno | dname | loc |
+-----+--------+----------+
| 10 | OxYBKa | RmIIrFfJ |
| 11 | hHSuuQ | XeQeXBQA |
| 12 | joSySV | XgIYXRek |
| 13 | VczriP | CtomqUEn |
| 14 | zKftFU | LUrYWLTn |
| 15 | FpEiaC | NiAfYDVX |
| 16 | dtOMuQ | SVXeAsqu |
| 17 | fpkdKv | aNQPDARK |
| 18 | aUBasR | gecaTwDD |
| 19 | jggjCp | OfehyaDT |
| 20 | LbSqYW | PmJPVoDe |
| 21 | IfAegE | GsYQlDnA |
| 22 | QEAPAi | kCltqsVD |
| 23 | dGXTDo | EjhgjAga |
| 24 | HovrsR | ilIIsQbG |
| 25 | fELRfW | wszxPHSu |
| 26 | uONAoO | hesLENdc |
| 27 | aUzOxY | yAilGzGH |
| 28 | sWCXja | ADrTyMqq |
| 29 | FiXtbW | GtcaVHyy |
| 30 | XsVBVb | rEYgIaac |
| 31 | jMmXgI | dollxJfu |
| 32 | MBvAsm | dHhHUEnx |
| 33 | EFrMMC | CeKsJtSj |
| 34 | nNegsz | vGRuxedf |
| 35 | ncuToL | PUfNDEmu |
| 36 | qrKCLX | GrLIiOxX |
| 37 | yyaBIQ | faKDNhes |
| 38 | NMznNf | izeSfVrT |
| 39 | uwaGlk | eiJchBrb |
+-----+--------+----------+
30 rows in set (0.05 sec)
-- 其他表可以 进行 写操作,
mysql> delete from dept where dno=10;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
|
总结: 会话0给A表加了锁, 其他会话的操作;
a.可以读其他表(A表以外的表) 进行读写;
b.对A表, 可以读, 但是写操作需要等待A会话0去释放了锁;
释放锁: unlock tables;
2)加写锁:
会话0:
lock table tablelock write;
当前会话(会话0)可以对加了写锁的表, 进行任何操作(增删改查);
但是不能操作(增删改查)其他表;
其他会话:
对会话0中加写锁的表, 可以增删改查的前提是: 等待会话0释放写锁;
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/* 加写锁 */
lock table tablelock write;
/* 不能对其他表进行任何操作 */
/* ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'dept' was not locked with LOCK TABLES */
select count(1) from dept;
|
MySQL表级锁的锁模式
- MyISAM 在执行查询语句(Select)前,会自动给涉及的所有表加读锁
- MyISAM 在执行更新操作(DML)前,会自动给涉及的表加写锁
- 对 MyISAM 表进行读操作
- 其他进程对同一表的操作
- 只有读锁释放后,才会执行其他进程的写操作
- 对 MyISAM 表进行写操作
- 其他进程对同一表操作
- 只有写锁释放后,才会执行其他进程的写操作
分析表锁定:
1)查看哪些表加了锁: show open tables; 1代表被加了锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
mysql> show open tables;
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
| Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked |
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
| testdata | dept | 0 | 0 |
| testdata | tablelock | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | general_log | 0 | 0 |
| db001 | t_book | 0 | 0 |
| testdata | emp | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | proc | 0 | 0 |
| mysql | event | 0 | 0 |
+----------+-------------+--------+-------------+
7 rows in set (0.05 sec)
|
2)分析表锁定的严重程度: show status like ’table%’;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mysql> show status like 'table%';
+----------------------------+--------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------------+--------+
| Table_locks_immediate | 800232 |
| Table_locks_waited | 1 |
| Table_open_cache_hits | 800056 |
| Table_open_cache_misses | 2 |
| Table_open_cache_overflows | 0 |
+----------------------------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.02 sec)
|
Table_locks_immediate: 即可能获取到的锁;
Table_locks_waited: 需要等待的表锁数; (waited的值越大, 代表锁的竞争越大)
小结
-
查看哪些表加了锁
-
分析表锁定的严重程度
-
1
|
show status like '%table%'
|
Table_locks_immediate 能够获取到的锁Table_locks_waited 需要等待的锁
-
1
|
Table_locks_immediate/Table_locks_waited> 5000
|
- 建议采用 InnoDB 引擎
- 否则使用 MyISAM 引擎
- 能够获取到的资源充分时,使用行锁,因此采用 InnoDB
行锁
默认代表是InnoDB;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
create table linelock
(
id int(5) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
)engine=innodb;
insert into linelock(name) values('1');
insert into linelock(name) values('2');
insert into linelock(name) values('3');
insert into linelock(name) values('4');
insert into linelock(name) values('5');
set autocommit=0;
/* 当前会话操作第 6 行 */
insert into linelock values(6, 'a6');
/* 其他会话操作第 6 行 */
/* 无法操作,需要等待锁释放 */
update linelock set name='ax' where id=6;
/* 其他会话操作第 8 行,没有锁,可以操作 */
insert into linelock values(8, 'a8');
|
会话0:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
mysql> insert into linelock values(6, 'a6');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from linelock;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | a6 |
+----+------+
6 rows in set (0.03 sec)
|
会话1:
1
2
|
mysql> update linelock set name='ax' where id=6;
1205 - Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
|
行锁: 操作相同的数据;
会话0: 写操作
insert into linelock values(6, ‘a6’);
会话1: 写操作, 同样的数据
update linelock set name=‘ax’ where id=6;
- 某个会话对一行数据进行 DML 操作时,其他会话需要等待锁释放
- 释放锁
- 表锁:
unlock tables; 或 commit/rollback 事务提交
- 行锁:
commit/rollback 事务提交(行锁是通过事务解锁)
行锁:操作不同的数据;
会话0:写操作
insert into linelock values(8, ‘a8’);
会话1:写操作, 操作不同的数据
update linelock set name=‘ax’ where id=5;
行锁, 一次锁一行数据; 因此 如果操作的是不同的数据,则不干扰;
行锁的注意事项
a.如果没有索引,则行锁会转变为表锁;
show index from linelock;
alter table linelock add index idx_linelock_name(name) ;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
show index from linelock;
/* 为 name 列增加索引 */
alter table linelock add index idx_linelock_name(name);
/* 当前会话操作 name='3' 的行 */
update linelock set name='a3x' where name='3';
/* 其他会话操作 name='4' 的行 */
/* name 列索引有效,不同的行操作互不影响 */
update linelock set name='a4x' where name='4';
/* 当前会话操作 name=3 的行 */
/* name 列是 varchar 类型,而 3 是整数类型,类型转换时索引失效,行锁转为表锁 */
update linelock set name='a3x' where name=3;
/* 其他会话操作 name='4' 的行 */
/* name 列索引失效,表被锁定,无法操作 name='4' 行,需要等待锁释放 */
update linelock set name='a4x' where name='4';
|
会话0:
update linelock set name=‘a3x’ where name=3;
会话1:
update linelock set name=‘a4x’ where name=‘4’;
– 可以发现, 数据被阻塞了(加锁);
– 原因:如果索引类 发生类类型转换, 则索引失效。因此此次操作会从行锁转变为表锁;
b.行锁的一种特殊情况: 间隙锁: 值在范围内, 但却不存在;
1
2
3
4
5
|
/* 不存在 id=7 的数据,此时 MySQL 会自动加上间隙锁 */
update linelock set name='x' where id>1 and id<9;
/* 其他会话操作 id=7 需要等待锁释放 */
insert into linelock value(7, 'a7');
|
加了个间隙锁(行锁);
行锁:
- InnoDB默认采用行锁;
- 缺点: 比表锁性能损耗大;
- 优点大: 并发能力强, 效率高;
- 因此建议, 高并发用InnoDB, 否则用MyISA;
行锁分析:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mysql> show status like '%innodb_row_lock%';
+-------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------------------+-------+
| Innodb_row_lock_current_waits | 0 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time | 51042 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time_avg | 51042 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time_max | 51042 |
| Innodb_row_lock_waits | 1 |
+-------------------------------+-------+
5 rows in set (0.03 sec)
|
| 类型 |
说明 |
| Innodb_row_lock_current_waits |
当前正在等待锁的进程数量 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time |
从系统启动到现在,等待总时长 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time_avg |
从系统启动到现在,平均等待时长 |
| Innodb_row_lock_time_max |
从系统启动到现在,最大等待时长 |
| Innodb_row_lock_waits |
从系统启动到现在,等待次数 |
查询行锁
1
2
3
4
5
|
/* for update 为查询语句加锁 */
select * from linelock where id=2 for update;
/* 其他会话操作该行要等待锁释放 */
update linelock set name='x' where id=2;
|
- 通过 for update 对 query 语句加锁;(如果仅仅是查询数据, 能否加锁? 可以, 要用for update)
- 关闭事务自动提交的三种方式
set autocommit =0;start transaction;begin;
参考资料
https://bigablecat.github.io/#/docs/courses/yanqun/yanqun_mysql
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25648377
https://www.cnblogs.com/xk920/p/11132038.html




